The 3D Printing Revolution: What to Expect in the Coming Decades
The Evolution of 3D Printing
The journey of 3D printing started as a niche technology used primarily for prototyping, but it has evolved significantly. The technology has moved from a novelty to a disruptive force across various industries, promising to change how we create, manufacture, and even think about objects.
From Rapid Prototyping to Disruptive Technology: The story of 3D printing began with its roots in rapid prototyping. Initially, it was a tool for engineers and designers to quickly create physical models of their concepts. However, it didn’t take long for the technology to expand its horizons and become a full-fledged manufacturing method.
Accessibility and Adoption: What sets this technology apart is its increasing accessibility. 3D printers, once prohibitively expensive, have become affordable for businesses and individuals alike. This democratization of manufacturing is at the core of the 3D printing revolution.
The Promise of 3D Printing Technology
The promise of 3D printing lies in its potential to democratize manufacturing. The technology allows us to design and produce objects with a level of complexity and customization that was previously inconceivable. It holds the key to transforming traditional manufacturing processes and making them more sustainable, efficient, and accessible.
Democratizing Manufacturing: In the past, manufacturing was the domain of large factories and corporations. 3D printing turns this paradigm on its head by enabling anyone with a 3D printer to become a manufacturer. This shift is empowering entrepreneurs, small businesses, and even hobbyists to create and innovate.
Complexity and Customization: Traditional manufacturing techniques often come with limitations in terms of complexity and customization. 3D printing has no such limitations. Objects can be designed with intricate geometries and tailored to individual needs. This opens up a world of possibilities in design and functionality.
How 3D Printing Works
To understand the revolution, it’s essential to grasp the basics of how 3D printing works. It’s a process known as additive manufacturing, where objects are built layer by layer. This method is in stark contrast to traditional subtractive manufacturing, which involves cutting or drilling materials to create objects.
Layer-by-Layer Creation: 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, depositing material on each layer until the entire object is complete. This additive approach is not only more flexible but also generates less waste compared to traditional subtractive methods.
Diverse Printing Technologies: 3D printing encompasses various printing technologies, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and more. Each technology has its unique advantages and applications.
Current Applications

3D Printing in Manufacturing
Customization in Mass Production: Manufacturing has been revolutionized by 3D printing. In industries like aerospace and automotive, 3D printing allows for mass customization. Parts can be tailored to specific requirements, improving performance and reducing waste.
Shortening Product Development Cycles: Traditional manufacturing often involves long lead times for tooling and molding. 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping and shorter product development cycles, giving companies a competitive edge.
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, 3D printing is a game-changer. It allows for the creation of complex and lightweight components, reducing the weight of aircraft and improving fuel efficiency. From jet engine parts to custom-designed brackets, 3D printing is soaring to new heights.
Lightweight Structures: Weight is a critical factor in aerospace design. 3D printing enables the production of lightweight, high-strength components that are essential for fuel efficiency and performance.
Complex Geometries: Aerospace components often require intricate geometries. 3D printing can produce these complex shapes with ease, improving the functionality of parts and reducing assembly requirements.
Automotive
The automotive sector harnesses 3D printing to revolutionize production processes. Customized parts, rapid prototyping, and even the possibility of printing entire car bodies are becoming a reality. As the industry seeks to reduce waste and enhance sustainability, 3D printing offers solutions.
Customized Components: From custom engine parts to unique interior elements, 3D printing enables the automotive industry to cater to individual preferences.
Sustainable Manufacturing: 3D printing supports sustainability in the automotive sector by reducing material waste and optimizing designs for fuel efficiency.
Consumer Goods
From customized smartphone cases to unique home decor, 3D printing has made its way into the lives of consumers. This technology is ushering in a new era of personalization, where individuals can design and create their own products with ease.
Personalized Products: Whether it’s a personalized phone case or a custom-designed piece of jewelry, 3D printing allows consumers to express their individuality.
Home Decor and Art: Decorative items, art pieces, and even furniture are being crafted through 3D printing, giving consumers the opportunity to adorn their homes with unique designs.
Healthcare and Bioprinting
Prosthetics and Implants
3D printing is transforming the healthcare industry by allowing the creation of patient-specific prosthetics and implants. Whether it’s a custom-made prosthetic limb or a personalized dental implant, the technology enhances patient care and quality of life.
Tailored to Individuals: Traditional prosthetics and implants can be generic in design. With 3D printing, each device can be customized to perfectly fit the patient, improving comfort and functionality.
Patient-Centric Care: The healthcare sector is increasingly adopting a patient-centric approach, and 3D printing aligns perfectly with this philosophy. It enables healthcare providers to offer highly personalized solutions.
Custom Medications
Pharmaceutical companies are exploring 3D printing for creating personalized medications. This could revolutionize the way we take drugs, ensuring that individuals receive precise dosages tailored to their specific needs.
Precise Dosages: Traditional medication may not always provide the exact dosage required for an individual. 3D printing allows the creation of precise dosages, enhancing the effectiveness of treatments.
Complex Drug Combinations: Some conditions require complex combinations of medications. 3D printing can combine multiple drugs into a single dosage, simplifying treatment regimens.
Organ Transplants
The most groundbreaking application of 3D printing in healthcare is the potential for bioprinting organs. While this technology is still in its early stages, it holds the promise of solving the organ shortage crisis.
Custom-Made Organs: With bioprinting, organs can be created to match a patient’s unique biological characteristics, reducing the risk of rejection and complications.
Shortening Transplant Waiting Lists: The ability to print organs on demand could significantly reduce transplant waiting lists and save countless lives.
Architecture and Construction
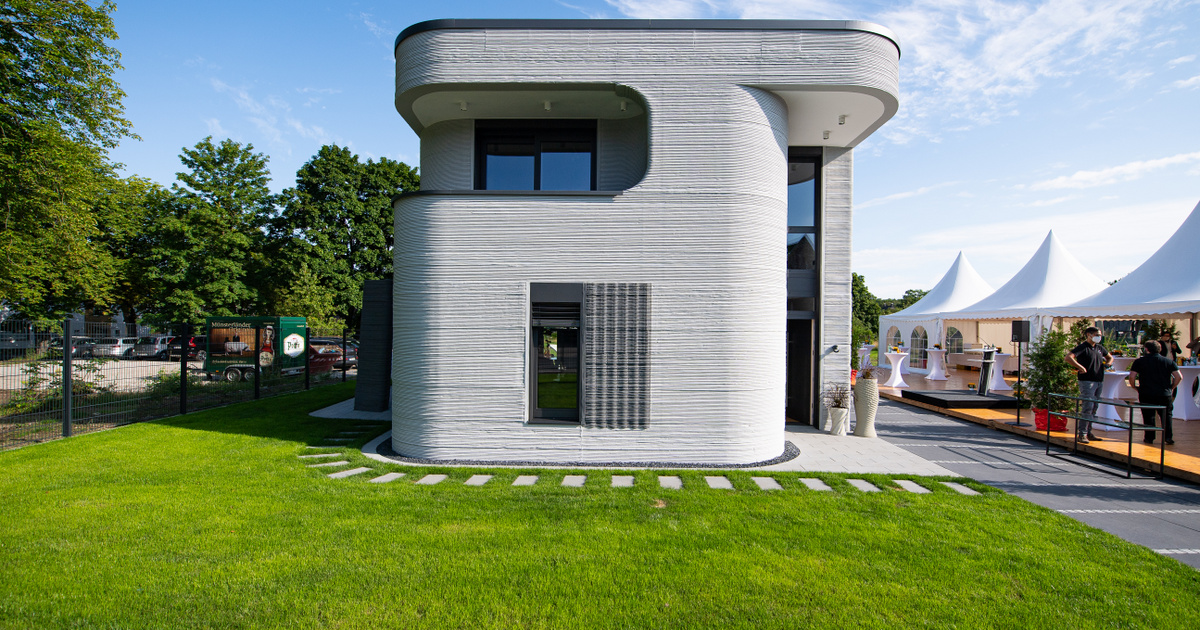

3D-Printed Homes
3D printing is poised to disrupt the construction industry by offering an innovative approach to building homes. Large-scale 3D printers can create entire houses with incredible speed and cost-efficiency.
Sustainable Building: 3D-printed homes often involve the use of sustainable materials. This approach aligns with the growing demand for eco-friendly construction methods.
Affordable Housing Solutions: 3D printing can address housing shortages by providing affordable housing options, especially in regions where housing is a critical issue.
Education and Prototyping
STEM Education
STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education benefits from 3D printing. It provides students with hands-on experience and encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and innovation.
Hands-On Learning: 3D printing engages students by allowing them to turn their ideas into tangible objects, making abstract concepts come to life.
Rapid Prototyping in Education: Teachers and students can use 3D printing for rapid prototyping of design concepts, giving students a taste of the iterative design process.
Rapid Prototyping
3D printing is revolutionizing the prototyping process across industries. It enables the quick and cost-effective production of prototypes, allowing designers and engineers to refine their concepts efficiently.
Iterative Design: With 3D printing, designers can rapidly iterate on their prototypes, making improvements and refinements with each iteration.
Reduced Development Costs: Traditional prototyping methods can be costly and time-consuming. 3D printing reduces both costs and time, allowing for faster product development.
The Future of 3D Printing

Advanced Materials
The future of 3D printing holds exciting developments in materials. Advanced materials are being developed to expand the capabilities of 3D printing technology.
Metal 3D Printing: The ability to 3D print with metals is a game-changer, opening up new possibilities in industries where high-strength metal parts are essential.
Bioinks and Tissue Engineering: In healthcare, bioprinting is advancing with the development of bioinks that can print living tissues. This has profound implications for regenerative medicine.
Sustainable Filaments: The quest for sustainability continues, and 3D printing materials are no exception. Sustainable filaments made from recycled plastics and eco-friendly sources are emerging.
Mass Customization
One of the defining features of 3D printing is mass customization. This concept is poised to disrupt industries ranging from fashion to healthcare.
Customized Fashion: Fashion designers are embracing 3D printing to create clothing, accessories, and footwear tailored to individual preferences and sizes.
Personalized Healthcare Products: From custom orthopedic insoles to bespoke dental implants, 3D printing is changing the way healthcare products are designed and manufactured.
On-Demand Manufacturing: 3D printing allows for on-demand production, reducing the need for large inventories and minimizing waste.
Localized Production
The ability to print objects on-site has significant implications for localized production. This concept is reshaping supply chains and reducing the environmental footprint of shipping.
Supply Chain Transformations: 3D printing enables decentralized and localized production, reducing the need for long and resource-intensive supply chains.
Space Exploration and Colonization
3D Printing in Space
In the realm of space exploration, 3D printing is a game-changer. It allows astronauts to create tools and components on the fly, reducing the need to transport everything from Earth.
Lunar and Martian Habitats: 3D printing is being explored as a method for creating habitats on the Moon and Mars. The technology could be instrumental in future colonization efforts.
Environmental Impact
Reduced Waste
Traditional manufacturing often generates significant waste. 3D printing reduces waste by creating objects layer by layer, using only the material necessary for the object.
Sustainable Design: 3D printing encourages sustainable design practices. Designers can optimize their creations to minimize material use while maximizing functionality.
Intellectual Property and Regulation
Copyright Challenges
The digital nature of 3D printing files poses copyright challenges. Protecting intellectual property in a world of digital sharing is a complex issue.
Regulatory Frameworks: Governments and regulatory bodies are working to develop frameworks that address copyright issues while still allowing for the open-source sharing of designs.
Challenges and Concerns
Environmental and Ethical Concerns
E-Waste and Recycling: The proliferation of 3D printing could lead to an increase in electronic waste. Solutions for recycling and responsible disposal are being explored.
Bioethical Considerations
The use of bioprinting raises ethical questions about the creation and use of living tissues. Bioethicists are exploring the implications and potential guidelines for this groundbreaking field.
Security and Cyberthreats
Counterfeit Production
The ease of producing goods with 3D printers raises concerns about counterfeit production. Companies and regulatory agencies are working to combat counterfeit products and protect consumers.
Cybersecurity Risks
The digital nature of 3D printing files opens up potential cybersecurity risks. Protecting intellectual property and ensuring safe 3D printing experiences are challenges for the industry.
Workforce Disruption
Job Transformations
The introduction of 3D printing into manufacturing and other industries is transforming job roles. Traditional manufacturing workers are being upskilled to operate 3D printers and work with digital design software.
Reskilling and Education Needs
As the workforce evolves, reskilling and education become crucial. Preparing the workforce for the digital age is a priority to ensure a smooth transition to the era of 3D printing.
Collaborative and Open-Source Efforts
Makerspaces and Fab Labs
Makerspaces and fab labs have become hubs for innovation. These community-driven spaces offer access to 3D printers and foster grassroots innovation.
Grassroots Innovation
The maker movement encourages individuals to tinker, experiment, and innovate. It’s a bottom-up approach to solving problems and creating new products.
Open-Source 3D Printing
Open-source 3D printing projects, like the RepRap Project, have played a significant role in making the technology accessible to a wider audience. Collaboration and shared knowledge drive progress.
Maker Movement
The maker movement is more than just a hobby. It’s a cultural shift that embraces collaboration, open sharing, and a DIY spirit. Makers are at the forefront of innovation.
Collaborative Initiatives
Collaboration is a driving force behind the 3D printing revolution. Companies, individuals, and even competitors are working together to advance the technology.
Crowdsourced Designs
Crowdsourcing has become a powerful tool in 3D printing. Communities come together to solve challenges, share designs, and collectively drive innovation.
Distributed Manufacturing Networks
The concept of distributed manufacturing envisions a future where goods are produced locally or even in the home. 3D printing plays a pivotal role in this vision.
Case Studies
The Impact of 3D Printing in Healthcare
Real-World Examples
Custom Prosthetics: Organizations like e-NABLE have used 3D printing to create customized prosthetic limbs for those in need.
Sustainability Achievements
Reducing Medical Waste: Hospitals and healthcare providers are exploring 3D printing to produce medical devices and implants on-site, reducing waste.
Companies Leading the Way
Organovo: Organovo is at the forefront of bioprinting, focusing on creating living tissues for drug testing and transplantation research.
Advancements in Aerospace
3D-Printed Aircraft Components
Major aerospace companies like Boeing and Airbus are incorporating 3D-printed components into their aircraft, reducing weight and enhancing fuel efficiency.
Education and Innovation
Success Stories in STEM Education
STEM education programs around the world are using 3D printing to engage students and foster innovative thinking.
The Future of 3D Printing Ecosystem
Industry Projections
The 3D printing industry is poised for significant growth, with projections indicating a substantial increase in market size.
Market Growth
The 3D printing market is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing adoption across industries and a growing consumer market.
Key Players
Key players in the 3D printing industry, like Stratasys, 3D Systems, and HP, are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Consumer Adoption
As 3D printers become more affordable and user-friendly, consumer adoption is on the rise.
Home 3D Printing
A new frontier in 3D printing is the rise of home 3D printers, allowing consumers to bring their ideas to life from the comfort of their homes.
3D-Printed Consumer Products
From home decor to custom fashion, 3D-printed consumer products are becoming increasingly popular.
Art and Creativity
Artists and 3D Printing
Artists are using 3D printing to create unique sculptures, installations, and art pieces that challenge traditional notions of creativity.
3D-Printed Art Installations
Museums and galleries are embracing 3D-printed art installations, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the art world.
Social and Cultural Impact
The rise of 3D printing is not just technological; it’s a cultural shift that empowers individuals to create, innovate, and participate in the production of goods.
Empowering Innovators
The 3D printing revolution empowers innovators, entrepreneurs, and creators to turn their ideas into reality with unprecedented ease.
Changing Design Paradigms
Designers are reimagining what’s possible, breaking free from the constraints of traditional manufacturing.
Conclusion
The Ongoing 3D Printing Revolution
The 3D printing revolution is an ongoing transformation that promises to reshape industries, empower individuals, and unlock a world of creative possibilities. As the technology continues to evolve, it will challenge the status quo, drive innovation, and redefine how we create and interact with the world around us. Preparing for this transformed future means embracing change, fostering collaboration, and staying at the forefront of a technological revolution that shows no signs of slowing down. Whether you’re a maker, a designer, an entrepreneur, or an industry leader, the 3D printing revolution offers a world of opportunities, and the journey is just beginning.
FAQ – The 3D Printing Revolution
Welcome to our FAQ section on the 3D printing revolution. Here, we address common questions about 3D printing, its impact, and what to expect in the coming decades.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from digital files by layering material on top of material. It’s a revolutionary technology that enables the production of complex and customized objects.
How does 3D printing work?
3D printing works by creating objects layer by layer from a digital model. It typically involves the use of a 3D printer, which deposits material according to the design provided, gradually building the final product.
What are the current applications of 3D printing?
3D printing has applications in various industries, including manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, healthcare, architecture, education, and more. It’s used for rapid prototyping, custom prosthetics, and even 3D-printed homes.
What is bioprinting, and how does it work?
Bioprinting is a subset of 3D printing that involves the layer-by-layer assembly of biological materials to create living tissues and, potentially, organs. It’s a groundbreaking area of research with the potential to revolutionize healthcare.
How does 3D printing impact sustainability?
3D printing reduces waste by producing objects layer by layer, using only the necessary material. It also encourages sustainable design practices and local production, which can minimize environmental impact.
What challenges does 3D printing face?
Challenges include intellectual property and copyright issues, regulatory frameworks, environmental concerns, cybersecurity risks, workforce disruptions, and more.
What is the maker movement, and how does it relate to 3D printing?
The maker movement is a cultural shift that embraces collaboration, open sharing, and a DIY spirit. It’s closely related to 3D printing because it fosters innovation and grassroots problem-solving, often through the use of 3D printers.
Who are the key players in the 3D printing industry?
Key players include companies like Stratasys, 3D Systems, HP, and a growing number of startups that are pushing the boundaries of 3D printing technology.
How can I get involved in the 3D printing revolution?
Getting involved can be as simple as exploring 3D printing for personal projects, joining a makerspace, or learning about 3D design and printing. There are online communities and resources to help you get started.
What’s the future of 3D printing?
The future holds exciting developments in advanced materials, mass customization, localized production, and continued growth in various industries. It’s a transformative technology that promises to redefine how we create and interact with the world.
What’s the role of 3D printing in space exploration?
3D printing is essential in space exploration as it enables astronauts to create tools and components in space. It’s also being explored as a method for creating habitats on the Moon and Mars.
How is 3D printing used in education?
3D printing is used in education to engage students, teach critical thinking, and provide hands-on learning experiences. It’s a valuable tool in STEM education and encourages innovation.
How can 3D printing change the healthcare industry?
3D printing in healthcare offers the potential for custom prosthetics, bioprinted organs, and reducing medical waste. It’s revolutionizing patient-specific care and medical research.
Is 3D printing impacting the art world?
Absolutely. Artists are using 3D printing to create unique sculptures, installations, and art pieces. It’s pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the art world.
How is 3D printing impacting consumer products?
3D printing is giving rise to personalized consumer products, including custom fashion, home decor, and accessories. It allows consumers to have a say in the design of their products.
What ethical considerations are associated with 3D printing?
Ethical considerations include issues related to bioprinting, intellectual property, environmental sustainability, and ensuring that technology benefits society as a whole.
What’s the relationship between 3D printing and sustainability?
3D printing contributes to sustainability by reducing waste, enabling local production, and promoting sustainable design practices. It aligns with the growing demand for eco-friendly manufacturing.
How can I protect my intellectual property in a world of 3D printing?
Protecting intellectual property involves understanding copyright issues, working within regulatory frameworks, and exploring creative solutions to safeguard your designs.
Is 3D printing affordable for individuals and small businesses?
Yes, 3D printers are becoming more affordable and user-friendly, making them accessible to individuals, makers, and small businesses.
How can I stay updated on the latest developments in 3D printing?
You can stay updated by following industry news, joining online communities, attending 3D printing events and conferences, and exploring educational resources related to 3D printing.
For more insights into the latest technology trends and innovative ideas, be sure to explore our blog at Sparking Ideas Web. Our blog covers a wide range of topics, including 3D printing, that can spark your curiosity and keep you informed about the ever-evolving world of technology and innovation.
To dive deeper into the 3D printing revolution and its impact on various industries, check out the Harvard Business Review article titled “The 3-D Printing Revolution” at HBR. This insightful article provides an in-depth analysis of how 3D printing is reshaping business and manufacturing, making it a must-read for anyone interested in the topic.





Uma resposta